» Articles
Electromagnetic pollution

With the development of technologies such as radars, radios, televisions and mobile phones, the use of electromagnetic radiation exponentially increased and in our cities transmitting antennas for the reproduction of such signals are everywhere. This rapid growth of these issuers produced a substantial increase in the electromagnetic radiation to which we are all subjected, necessitating the implementation of oversight policies and to evaluate the electromagnetic pollution to which we are subjected and to monitor the quality of individual signals and their coverage territory. On July, 1st 2016, the EU states will have to implement through national laws, the European Directive 2013/35/EU which establishes minimum health and safety requirements..
Continue reading
Directive 2013/35/EU
The directive 2013/35/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to risks arising from physical agents (electromagnetic fields), repeals the Directive 2004/40/CE. This new directive, released on 26 June 2013, according to studies made by the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) obliges EU countries to implement this legislation no later than 1 July 2016. Until now companies and employers have been able to make measurements at their discretion, but from the entry into force of the standard..
Continue reading
Contact current
In the workplace and in the world we live in, the electric and magnetic fields are always present. These can have a natural origin (electrostatic charge, terrestrial magnetism) or artificial (electrical equipment or systems of distribution of electricity). Industrial development and the use of advanced technology has produced in recent years a considerable increase of artificial electromagnetic fields, making it necessary to study theirs effects and regulate theirs exposure to protect the health of workers and the public. Thanks to studies of ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection), based on the most authoritative scientific results..
Continue reading
Anechoic chamber
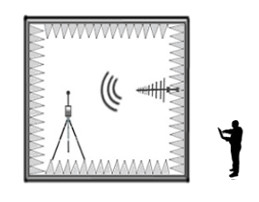
The anechoic chamber is a specific test environment for radio frequency signals (RF) and microwave (MW) used to make measurements of electromagnetic fields without any outside interference. Its size varies greatly depending on the field of application and the frequencies used in it. The anechoic chamber is used to perform measurements in the study of acoustics and electromagnetic fields. Anechoic means no echo and this property is made by coating the walls with absorber material to compensate all the reflections of the electromagnetic wave. For the inner lining are used two types of materials ..
Continue reading
Electromagnetic shielding
The electromagnetic shielding allows to attenuate the electromagnetic fields produced by machinery, industrial processes or antennas. For example in every hospital or clinic where there is an MRI is necessary that the room used is fully screen to avoid artifacts in the images of the examination of resonance. Another environment which requires an electromagnetic shielding is the anechoic chamber that must be shielded completely from any external influence that may affect the data collection. At the same time the shield prevents the escape of the generated fields. To obtain an electromagnetic shielding is used a Faraday cage. This is made..
Continue reading
Safety at work

Safety at work and therefore the operator's exposure to risk during the course of his job is a strongly felt aspect in the work, so there is a regulation in flux in order to meet the ever increasing demands of protection of workers. n the sector of electromagnetic fields a worker is continually subject to physical agents that, in the long run could lead to the onset of very bad diseases. Although we currently do not have scientific evidence that established the existence of a causal relationship between the electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields with the onset of this type of serious diseases, the European Parliament repealed the..